Whether replying to customers, preparing a product/service for the market, or managing internal departments day to day, efficiency in your business isn’t just an advantage—it’s a necessity. Companies striving to stay ahead of the competition must master streamlining their operations.
This is where business process design comes into play. It’s the strategic blueprint for transforming chaotic workflows into seamless, productive systems.
In this article, we’ll explore the principles and practices of business process design, revealing the secrets to crafting processes that meet and exceed organizational goals. Whether you’re overhauling existing procedures or building new ones from scratch, discover why process design is essential for your business and the eight fundamental principles that define its success.
What is business process design?
Business process design involves planning and improving organizational workflows. It maps out each task and optimizes it to reduce waste, promote efficiency, and optimize resource usage. When performed correctly, business process design facilitates smoother operations and seamless adaptations to customer needs and market changes.
Why is it important to understand process design?
Process design lets you evaluate how each process impacts your company’s operations and whether it contributes to objectives. Every process – and task within that process – contributes to productivity, efficiency, and employee engagement.
Failing to understand the design of each process can lead to a less coordinated approach across the entire organization, wasted resources, and unclear workflows. By prioritizing the development of effective business processes, it’s possible to achieve growth.
The three types of process design:
- Core Processes: Also known as operational processes, these are workflows within a business that generate revenue and offer products/services to customers. Examples include developing a product and processing orders.
- Strategic Processes: Strategic process design involves identifying weaknesses in processes that impact the long-term goals and vision of an organization. For example, performing market research and realigning the strategy to reach objectives.
- Management Processes: Operations management, compliance, and risk identification are all management processes. Any gaps or inefficiencies can impact the entire organization’s structure and productivity. Examples include introducing new equipment or strengthening compliance frameworks.
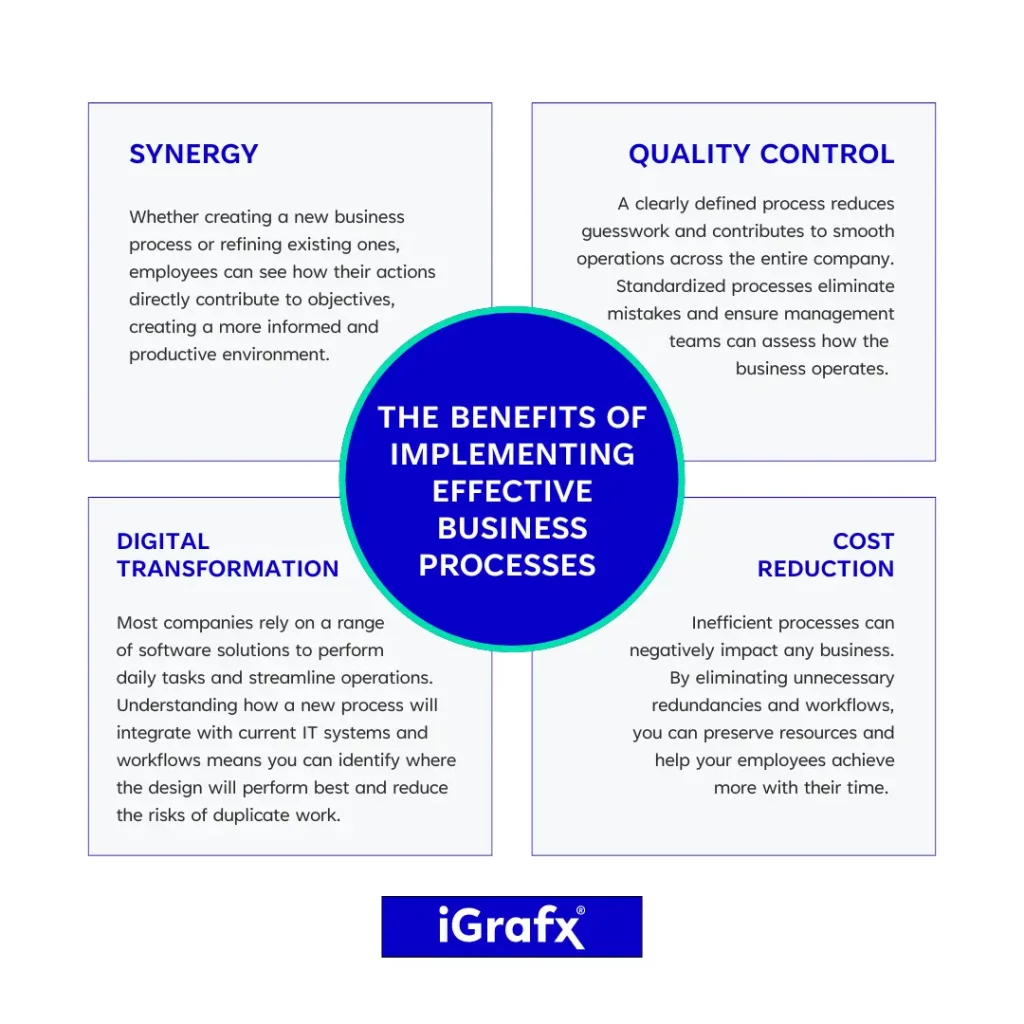
The benefits of implementing effective business processes
Business process design isn’t just about streamlining operations; it creates positive effects across your company. Let’s explore the many benefits of seamless processes.
Synergy
When everyone understands the objectives they’re working towards, it’s easier to monitor progress and accountability.
Whether creating a new business process or refining existing ones, employees can see how their actions directly contribute to objectives, creating a more informed and productive environment.
Quality control
A clearly defined process reduces guesswork and contributes to smooth operations across the entire company. Standardized processes eliminate mistakes and ensure management teams can assess how the business operates.
Once you identify areas for improvement, you can apply all rules and ensure they remain consistent.
Digital transformation
Most companies rely on a range of software solutions to perform daily tasks and streamline operations. Understanding how a new process will integrate with current IT systems and workflows means you can identify where the design will perform best and reduce the risks of duplicate work.
Cost reduction
Inefficient processes can negatively impact any business. According to HR Grapevine, the average employee wastes one month each year on unnecessary tasks and workflows, highlighting an ongoing problem.
By eliminating unnecessary redundancies and workflows, you can preserve resources and help your employees achieve more with their time.
The 7 Process design principles
Before you implement new processes or redesign your current processes, it’s essential to understand the key principles that define its success. Small businesses and large organizations with multiple departments should remember seven principles when optimizing processes.
1: Consumer-Centric
As a business, you’ll know your success lies in an ability to deliver positive outcomes and value for consumers or clients. Understanding how people will interact with your product or service ensures customer satisfaction.
2: Goal setting
Whether you’re introducing a new product, focusing on operations management, or developing a new workflow for employees, there has to be a clear goal in mind.
Are you solving an internal problem? What kind of value should your product create? Knowing your goals makes it easier to design effective processes.
3: Collaboration
Process design requires collaboration between key stakeholders. Departments and individual teams should share ideas and explore how the new process might impact the organization. By working together, teams can address potential challenges and ensure accountability.
4: Streamlining workflows
Evaluating each current process and identifying bottlenecks enables improvement opportunities. For example, are there delays in the supply chain? Do your employees go through unnecessary steps? Where can you automate specific workflows?
5: Standardization
Once you create an effective business process, you’ll need to set clear steps for employees. Doing this ensures they know how to complete each task and reduces errors. It’s also integral to quality control and isolating potential training opportunities.
6: Compliance
Every business must be aware of legal restrictions and monitor each process for compliance issues. While some industries are under stricter regulations, compliance management at individual and organizational levels protects the company from legal repercussions and reputation damage.
7: Ongoing improvement
Process design isn’t a one-time thing; it’s about constantly assessing and evolving each workflow to ensure optimal results. Taking a practical approach to reviewing your processes and evaluating whether they’re still functional can improve efficiency and produce better outcomes.
Four steps to creating an effective business process
So, now you know more about process design and its principles, it’s time to reveal how to create an efficient process that moves your organization towards set objectives. Following these crucial steps means you can build the process and monitor its effect on your business.
Step 1: Process design objectives
The first step in process design is to identify your business needs. Why are you thinking about creating a new process? Is it to improve operational efficiency? Or are you releasing a new product or service?
Understanding the why helps you focus on the what.
Consider why you’re creating a new process and assess its potential impact on employees and customers. Examine all elements of your company, including its mission, internal infrastructure, target audience, and long-term growth goals.
Step 2: Process mapping
Process mapping creates a visual representation of your current workflows, usually in mind map or flowchart format. Once you have the initial process map, you can add steps to create a new workflow.
Advanced software lets you create a process map that identifies the following touchpoints:
- Who starts the process?
- Which steps are involved?
- Which tasks occur within the process?
- What results does the process achieve?
- Who benefits from the process?
A well-designed process should eliminate bottlenecks and pain points. When analyzing your current workflows, ask people to review them and document any issues. This makes it easier to create a more effective business process.
Step 3: Process development
When developing a new process, make sure you involve all stakeholders. Managers and employees who will use the process regularly should have the opportunity to explain how each task within the process should improve and voice their concerns.
Look for new ideas and evaluate how they’ll improve the current process. Innovation and automation opportunities can remove boring tasks and give employees more time to focus on achieving wider productivity objectives.
Step 4: Test, adapt and evolve
Once you know the goals of the new process, it’s easier to create prototypes that test new workflows. Remember, this stage is often a case of trial and error, but integrating process simulation tools can help you create digital representations of each process and assess which offers the best outcomes.
The next step is to create the new process and ensure a transparent chain of information and instructions for everyone who uses it. Regularly testing if processes continue to be effective enables you to adapt and evolve them.
Potential challenges of process design
While process design offers numerous benefits, it also has some challenges. They’re not deal-breakers, but understanding potential issues can help mitigate risks and overcome barriers.
Overthinking steps
A process shouldn’t be time-consuming; it should get your team to their desired destination in as few steps as possible. You don’t need to over-complicate things by introducing other steps or placing limitations on workflows.
Ask key team members which steps are most important and assess how to cut unnecessary tasks.
Training
Training employees on new processes can be challenging, especially if they involve using technology. Developing comprehensive training programs and asking participants for feedback can identify areas that require more clarification.
Allowing employees to voice their concerns and ask questions about the new processes reduces their resistance to change.
Low adoption rates
A lack of training and resistance to change can contribute to low adoption rates. Other factors include fears that technology will result in job losses and failing to understand why the new process is essential for productivity.
Clarifying the purpose of each process and explaining its benefits will help your team develop their skills and contribute to achieving organizational objectives.
Ready to optimize your business processes?
Business process management unlocks future growth and ensures your organization stays ahead of the curve. When you redesign existing processes, it can enhance productivity and empower your team to adopt workflows that fuel growth.
Technology today removes the need for manual process monitoring, allowing businesses of all sizes to optimize for maximum efficiency and productivity.
Using a comprehensive business process management tool like Process360 Live can integrate discovery, process maps, design, and simulations into one convenient platform.
If you’d like a demo or free trial, please get in touch with us today.
FAQs
What is the meaning of process design?
Process design involves planning and improving workflows within an organization. It creates a roadmap for tasks to achieve goals, including waste reduction, resource optimization, and streamlined operations.
What is basic process design?
In simple terms, basic process design is similar to sketching an outline but not filling in the details. It assesses the fundamental steps in each process and identifies key decision points. Once you build the foundation of each workflow, you can fill in the details for a comprehensive system.
What is a process design model?
Process models are visual representations of an individual process and its tasks. These flowcharts outline steps, decision points, and how information flows between each touchpoint. Visualizing the process also enables you to identify and remove bottlenecks.
What can I use process design tools for?
Process design can improve internal and external processes. For example, you can assess how representatives handle customer queries or identify issues within your supply chain.
Industrial businesses can understand delays in the production process and implement automation to speed things up.
Why use process design software?
Mapping and redesigning business processes manually is an arduous task that involves a significant investment of time and expertise. There’s also more room for error. Process management software accurately visualizes each process and enables you to simulate changes.
It can integrate automation tools and allow key stakeholders to understand the purpose behind each process.